What is Exosome?
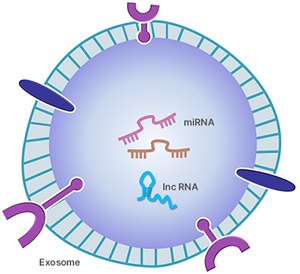
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles that have the ability to convey various types of molecules between cells
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles that have the ability to convey various types of molecules between cells.
These vesicles contain many constituents of a cell, including DNA, RNA, lipids, metabolites, and cytosolic and cell-surface proteins.
It is believed that the delivery of exosomal RNA molecules, which include both coding and non-coding RNAs, plays a role in cell-to-cell signaling.
Exosomal RNA has the potential to be used as a biomarker for identifying various diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, respiratory diseases, and inflammation.
Artificial intelligence technology is being utilized in many fields, and exosome-based disease diagnostics is no exception.
AI technologies can be used to discover and quantify exosomal RNA, analyze exosomal RNA data, and diagnose diseases related to exosomal RNA.
This plays an important role in disease diagnosis, biomarker discovery, and understanding biological processes.
-
CALTH will provide the following services using miRNA analysis using machine learning.
-
· Discover new diagnostic candidates and analyze exosomal RNA expression profile data for disease associations
-
· Identify diseases and disease subtypes through machine learning models
-
· Provide personalized care that considers the individual characteristics of patients
-
· Improve the diagnostic accuracy of disease diagnosis
-
· Predict prognosis and monitor patients